(Java programming Example for Beginners)
Java if, if…else Statement
In this tutorial, you will learn about control flow statements in Java using Java if and if…else statements with the help of examples.
In computer programming, it’s often desirable to execute a certain section of code based upon whether the specified condition is true or false (which is known only during the run time). For such cases, control flow statements are used.
Java if (if-then) Statement
In Java, the syntax of the if-then statement is:
if (expression) {
// statements
}
Here expression is a boolean expression. A boolean expression returns either true or false.
- if the expression is evaluated to
true, statement(s) inside the body ofif(statements inside parenthesis) are executed - if the expression is evaluated to
false, statement(s) inside the body ofifare skipped from execution
How if statement works?

Working of Java if statement
Example 1: Java if Statement
class IfStatement{
public static void main(String[] args){
int number = 10;
// checks if number is greater than 0
if (number > 0) {
System.out.println("The number is positive.");
}
System.out.println("This statement is always executed.");
}
}
Output:
The number is positive. This statement is always executed.
In the above example, we have a variable named number. Here, the test expression checks if the number is greater than 0 (number > 0).
Since the number is greater than 0. So the test expression evaluates to true. Hence code inside the body of if is executed.
Now, change the value of the number to a negative integer. Let’s say -5.
int number = -5;
If we run the above program with the new value of the number, the output will be:
This statement is always executed.
Here, the value of number is less than 0. So, the test expression number > 0 evaluates to false. Hence, the body of if is executed.
Note: We can also use strings as the boolean expression.
Example 2: Java if…else with String
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
// create a string variable
String language = "Java";
// if statement
if(language == "Java") {
System.out.println("This is best programming language.");
}
}
}Output
This is best programming language.
Here, we are comparing two strings in the if block.
Java if…else (if-then-else) Statement
The if statement executes a certain section of code if the test expression is evaluated to true. However, if the test expression is evaluated to false, it does nothing.
In this case, we can use an optional else block. Statements inside the body of else block are executed if the test expression is evaluated to false. This is known as the if-then-else statement in Java.
The syntax of the if-then-else statement is:
if (expression) {
// codes
}
else {
// some other code
}
Here, our program will do one task (task inside if block) if the test expression is true and another task (task inside else block) if the test expression is false.
How if…else statement works?
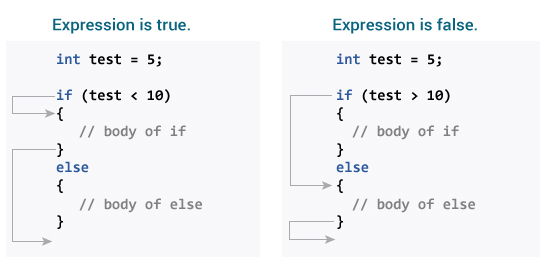
Working of Java if-else statements
Example 2: Java if else Statement
class IfElse{
public static void main(String[] args){
int number = 10;
// checks if number is greater than 0
if (number > 0) {
System.out.println("The number is positive.");
}
else {
System.out.println("The number is not positive.");
}
System.out.println("This statement is always executed.");
}
}
Output:
The number is positive. This statement is always executed.
In the above example, we have a variable named number. Here, the test expression checks if the number is greater than 0 (number > 0).
Since the value of the number is 10, the test expression evaluates to true. Hence code inside the body of if is executed.
Now, change the value of the number to a negative integer. Let’s say -5.
int number = -5;
If we run the program with the new value of the number, the output will be:
The number is not positive. This statement is always executed.
Here, the value of number is -5. So the test expression evaluates to false. Hence code inside the body of else is executed.
Java if..else..if Statement
In Java, we have an if…else…if ladder, that can be used to execute one block of code among multiple other blocks.
if (expression1) {
// codes
}
else if(expression2) {
// codes
}
else if (expression3) {
// codes
}
.
.
else {
// codes
}
Here, if statements are executed from the top towards the bottom. As soon as the test expression is true, codes inside the body of that the if statement is executed. Then, the control of the program jumps outside the if-else-if ladder.
If all test expressions are false, codes inside the body of else is executed.
Example 3: Java if..else..if Statement
class Ladder{
public static void main(String[] args){
int number = 0;
// checks if number is greater than 0
if (number > 0) {
System.out.println("The number is positive.");
}
// checks if number is less than 0
else if (number < 0) {
System.out.println("The number is negative.");
}
else {
System.out.println("The number is 0.");
}
}
}
Output:
The number is 0.
In the above example, we are checking whether the number is positive, negative or zero. Here, we have two test expressions:
number > 0– checks if the number is greater than 0number < 0– checks if the number is less than 0
Here, the value of number is 0. So both the test expression evaluates to false. Hence the statement inside the body of else is executed.
Java Nested if..else Statement
In Java, it is also possible to if..else statements inside a if..else statement. It’s called nested if...else statement.
Here’s a program to find largest of 3 numbers:
Example 4: Nested if…else Statement
class Number{
public static void main(String[] args){
// declaring double type variables
Double n1 = -1.0, n2 = 4.5, n3 = -5.3, largestNumber;
// checks if n1 is greater than or equal to n2
if (n1 >= n2) {
// if...else statement inside the if block
// checks if n1 is greater than or equal to n3
if (n1 >= n3) {
largestNumber = n1;
}
else {
largestNumber = n3;
}
}
else {
// if..else statement inside else block
// checks if n2 is greater than or equal to n3
if (n2 >= n3) {
largestNumber = n2;
}
else {
largestNumber = n3;
}
}
System.out.println("The largest number is " + largestNumber);
}
}
Output:
The largest number is 4.5
Java tutorials for Beginners – Java if, if…else Statement
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
