(Python Tutorial – 012)
Python while Loop
Loops are used in programming to repeat a specific block of code. In this article, you will learn to create a while loop in Python.
What is while loop in Python?
The while loop in Python is used to iterate over a block of code as long as the test expression (condition) is true.
We generally use this loop when we don’t know the number of times to iterate beforehand.
Syntax of while Loop in Python
while test_expression:
Body of while
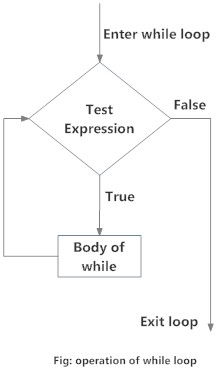
In the while loop, test expression is checked first. The body of the loop is entered only if the test_expression evaluates to True. After one iteration, the test expression is checked again. This process continues until the test_expression evaluates to False.
In Python, the body of the while loop is determined through indentation.
The body starts with indentation and the first unindented line marks the end.
Python interprets any non-zero value as True. None and 0 are interpreted as False.
Flowchart of while Loop
Example: Python while Loop
# Program to add natural
# numbers up to
# sum = 1+2+3+...+n
# To take input from the user,
# n = int(input("Enter n: "))
n = 10
# initialize sum and counter
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum = sum + i
i = i+1 # update counter
# print the sum
print("The sum is", sum)When you run the program, the output will be:
Enter n: 10 The sum is 55
In the above program, the test expression will be True as long as our counter variable i is less than or equal to n (10 in our program).
We need to increase the value of the counter variable in the body of the loop. This is very important (and mostly forgotten). Failing to do so will result in an infinite loop (never-ending loop).
Finally, the result is displayed.
While loop with else
Same as with for loops, while loops can also have an optional else block.
The else part is executed if the condition in the while loop evaluates to False.
The while loop can be terminated with a break statement. In such cases, the else part is ignored. Hence, a while loop’s else part runs if no break occurs and the condition is false.
Here is an example to illustrate this.
'''Example to illustrate
the use of else statement
with the while loop'''
counter = 0
while counter < 3:
print("Inside loop")
counter = counter + 1
else:
print("Inside else")Output
Inside loop Inside loop Inside loop Inside else
Here, we use a counter variable to print the string Inside loop three times.
On the fourth iteration, the condition in while becomes False. Hence, the else part is executed.
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
Learn by Coding: v-Tutorials on Applied Machine Learning and Data Science for Beginners
Latest end-to-end Learn by Coding Projects (Jupyter Notebooks) in Python and R:
All Notebooks in One Bundle: Data Science Recipes and Examples in Python & R.
End-to-End Python Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
End-to-End R Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
Applied Statistics with R for Beginners and Business Professionals
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in Python: Tabular Data Analytics
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in R: Tabular Data Analytics
Python Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
R Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
Comparing Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Python for Classification (FREE)
There are 2000+ End-to-End Python & R Notebooks are available to build Professional Portfolio as a Data Scientist and/or Machine Learning Specialist. All Notebooks are only $29.95. We would like to request you to have a look at the website for FREE the end-to-end notebooks, and then decide whether you would like to purchase or not.
R tutorials for Business Analyst – R While Loop with Example
Python Example – Write a Python program to sort Counter by value
