(C Programming Tutorials)
C User-defined functions
In this tutorial, you will learn to create user-defined functions in C programming with the help of an example.
C allows you to define functions according to your need. These functions are known as user-defined functions. For example:
Suppose, you need to create a circle and color it depending upon the radius and color. You can create two functions to solve this problem:
createCircle()functioncolor()function
Example: User-defined function
Here is an example to add two integers. To perform this task, we have created an user-defined addNumbers().
#include <stdio.h>
int addNumbers(int a, int b); // function prototype
int main(){
int n1,n2,sum;
printf("Enters two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d",&n1,&n2);
sum = addNumbers(n1, n2); // function call
printf("sum = %d",sum);
return 0;
}
int addNumbers(int a, int b) // function definition {
int result;
result = a+b;
return result; // return statement
}Function prototype
A function prototype is simply the declaration of a function that specifies function’s name, parameters and return type. It doesn’t contain function body.
A function prototype gives information to the compiler that the function may later be used in the program.
Syntax of function prototype
returnType functionName(type1 argument1, type2 argument2, ...);
In the above example, int addNumbers(int a, int b); is the function prototype which provides the following information to the compiler:
- name of the function is
addNumbers() - return type of the function is
int - two arguments of type
intare passed to the function
The function prototype is not needed if the user-defined function is defined before the main() function.
Calling a function
Control of the program is transferred to the user-defined function by calling it.
Syntax of function call
functionName(argument1, argument2, ...);
In the above example, the function call is made using addNumbers(n1, n2); statement inside the main() function.
Function definition
Function definition contains the block of code to perform a specific task. In our example, adding two numbers and returning it.
Syntax of function definition
returnType functionName(type1 argument1, type2 argument2, ...)
{
//body of the function
}
When a function is called, the control of the program is transferred to the function definition. And, the compiler starts executing the codes inside the body of a function.
Passing arguments to a function
In programming, argument refers to the variable passed to the function. In the above example, two variables n1 and n2 are passed during the function call.
The parameters a and b accepts the passed arguments in the function definition. These arguments are called formal parameters of the function.

The type of arguments passed to a function and the formal parameters must match, otherwise, the compiler will throw an error.
A function can also be called without passing an argument.
Return Statement
The return statement terminates the execution of a function and returns a value to the calling function. The program control is transferred to the calling function after the return statement.
In the above example, the value of the result variable is returned to the main function. The sum variable in the main() function is assigned this value.
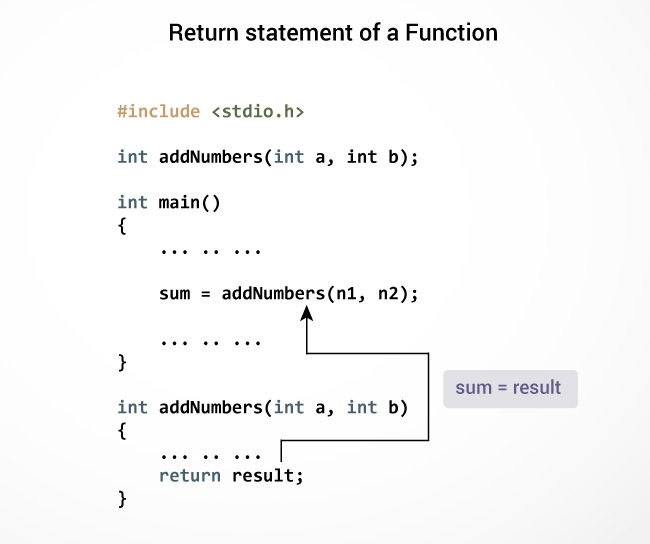
Syntax of return statement
return (expression);
For example,
return a; return (a+b);
The type of value returned from the function and the return type specified in the function prototype and function definition must match.
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
Learn by Coding: v-Tutorials on Applied Machine Learning and Data Science for Beginners
Latest end-to-end Learn by Coding Projects (Jupyter Notebooks) in Python and R:
All Notebooks in One Bundle: Data Science Recipes and Examples in Python & R.
End-to-End Python Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
End-to-End R Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
Applied Statistics with R for Beginners and Business Professionals
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in Python: Tabular Data Analytics
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in R: Tabular Data Analytics
Python Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
R Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
Comparing Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Python for Classification (FREE)
There are 2000+ End-to-End Python & R Notebooks are available to build Professional Portfolio as a Data Scientist and/or Machine Learning Specialist. All Notebooks are only $29.95. We would like to request you to have a look at the website for FREE the end-to-end notebooks, and then decide whether you would like to purchase or not.
C Example for Beginners: C Program to Check Prime or Armstrong Number Using User-defined Function
