(SQL tutorials for Business Analyst)
In this end-to-end example, you will learn – SQL Tutorials for Business Analyst: SQL | DDL, DML, TCL and DCL.
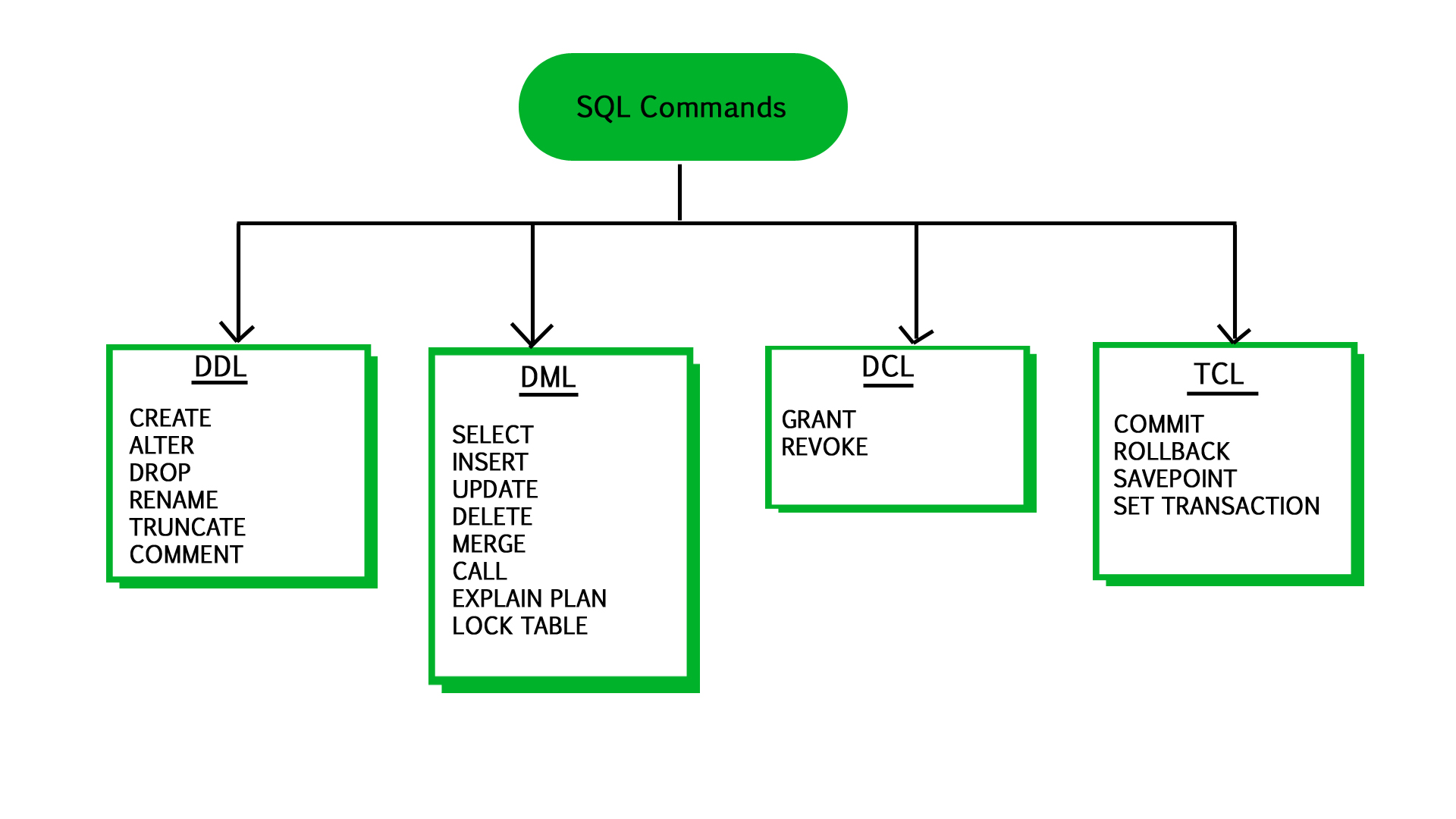
SQL | DDL, DML, TCL and DCL
In this article, we’ll be discussing Data Definition Language, Data Manipulation Language, Transaction Control Language, and Data Control Language.
DDL (Data Definition Language) :
Data Definition Language is used to define the database structure or schema. DDL is also used to specify additional properties of the data. The storage structure and access methods used by the database system by a set of statements in a special type of DDL called a data storage and definition language. These statements define the implementation details of the database schema, which are usually hidden from the users. The data values stored in the database must satisfy certain consistency constraints.
For example, suppose the university requires that the account balance of a department must never be negative. The DDL provides facilities to specify such constraints. The database system checks these constraints every time the database is updated. In general, a constraint can be an arbitrary predicate pertaining to the database. However, arbitrary predicates may be costly to the test. Thus, the database system implements integrity constraints that can be tested with minimal overhead.
- Domain Constraints : A domain of possible values must be associated with every attribute (for example, integer types, character types, date/time types). Declaring an attribute to be of a particular domain acts as the constraints on the values that it can take.
- Referential Integrity : There are cases where we wish to ensure that a value appears in one relation for a given set of attributes also appear in a certain set of attributes in another relation i.e. Referential Integrity. For example, the department listed for each course must be one that actually exists.
- Assertions : An assertion is any condition that the database must always satisfy. Domain constraints and Integrity constraints are special form of assertions.
- Authorization : We may want to differentiate among the users as far as the type of access they are permitted on various data values in database. These differentiation are expressed in terms of Authorization. The most common being :
read authorization – which allows reading but not modification of data ;
insert authorization – which allow insertion of new data but not modification of existing data
update authorization – which allows modification, but not deletion.
Some Commands:
CREATE : to create objects in database ALTER : alters the structure of database DROP : delete objects from database RENAME : rename an objects
Following SQL DDL-statement defines the department table :
create table department (dept_name char(20), building char(15), budget numeric(12,2));
Execution of the above DDL statement creates the department table with three columns – dept_name, building, and budget; each of which has a specific datatype associated with it.
DML (Data Manipulation Language) :
DML statements are used for managing data with in schema objects.
DML are of two types –
- Procedural DMLs : require a user to specify what data are needed and how to get those data.
- Declerative DMLs (also referred as Non-procedural DMLs) : require a user to specify what data are needed without specifying how to get those data.Declarative DMLs are usually easier to learn and use than procedural DMLs. However, since a user does not have to specify how to get the data, the database system has to figure out an efficient means of accessing data.
Some Commands :
SELECT: retrieve data from the database INSERT: insert data into a table UPDATE: update existing data within a table DELETE: deletes all records from a table, space for the records remain
Example of SQL query that finds the names of all instructors in the History department :
select instructor.name from instructor where instructor.dept_name = 'History';
The query specifies that those rows from the table instructor where the dept_name is History must be retrieved and the name attributes of these rows must be displayed.
TCL (Transaction Control Language) :
Transaction Control Language commands are used to manage transactions in the database. These are used to manage the changes made by DML-statements. It also allows statements to be grouped together into logical transactions.
Examples of TCL commands –
COMMIT: Commit command is used to permanently save any transaction
into the database.
ROLLBACK: This command restores the database to last committed state.
It is also used with savepoint command to jump to a savepoint
in a transaction.
SAVEPOINT: Savepoint command is used to temporarily save a transaction so
that you can rollback to that point whenever necessary.
DCL (Data Control Language) :
A Data Control Language is a syntax similar to a computer programming language used to control access to data stored in a database (Authorization). In particular, it is a component of Structured Query Language (SQL).
Examples of DCL commands :
GRANT: allow specified users to perform specified tasks. REVOKE: cancel previously granted or denied permissions.
The operations for which privileges may be granted to or revoked from a user or role apply to both the Data definition language (DDL) and the Data manipulation language (DML), and may include CONNECT, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, EXECUTE and USAGE.
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
Learn by Coding: v-Tutorials on Applied Machine Learning and Data Science for Beginners
Latest end-to-end Learn by Coding Projects (Jupyter Notebooks) in Python and R:
All Notebooks in One Bundle: Data Science Recipes and Examples in Python & R.
End-to-End Python Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
End-to-End R Machine Learning Recipes & Examples.
Applied Statistics with R for Beginners and Business Professionals
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in Python: Tabular Data Analytics
Data Science and Machine Learning Projects in R: Tabular Data Analytics
Python Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
R Machine Learning & Data Science Recipes: Learn by Coding
Comparing Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Python for Classification (FREE)
There are 2000+ End-to-End Python & R Notebooks are available to build Professional Portfolio as a Data Scientist and/or Machine Learning Specialist. All Notebooks are only $29.95. We would like to request you to have a look at the website for FREE the end-to-end notebooks, and then decide whether you would like to purchase or not.
MySQL Tutorials for Business Analyst: MySQL Create Database, Tables, Data Types
