
(Python Example for Beginners)
Write a NumPy program to compute the determinant of an array.
From Wikipedia: In linear algebra, the determinant is a value that can be computed from the elements of a square matrix. The determinant of a matrix A is denoted det(A), det A, or |A|. Geometrically, it can be viewed as the scaling factor of the linear transformation described by the matrix.
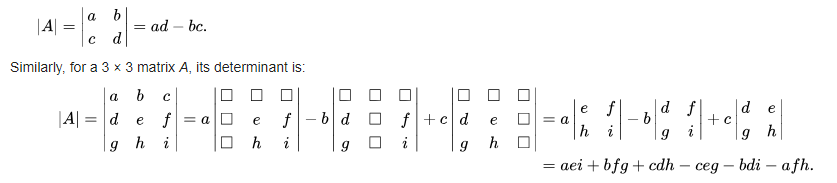
Sample Solution :
Python Code :
Sample Output:
Original array: [[1 2] [3 4]] Determinant of the said array: -2.0
Python Example – Write a NumPy program to compute the determinant of an array
Two Machine Learning Fields
There are two sides to machine learning:
- Practical Machine Learning:This is about querying databases, cleaning data, writing scripts to transform data and gluing algorithm and libraries together and writing custom code to squeeze reliable answers from data to satisfy difficult and ill defined questions. It’s the mess of reality.
- Theoretical Machine Learning: This is about math and abstraction and idealized scenarios and limits and beauty and informing what is possible. It is a whole lot neater and cleaner and removed from the mess of reality.
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
