(Java programming Example for Beginners)
Java break Statement
In this tutorial, you will learn about the break statement, labeled break statement in Java with the help of examples.
While working with loops, it is sometimes desirable to skip some statements inside the loop or terminate the loop immediately without checking the test expression.
In such cases, break and continue statements are used.
The break statement in Java terminates the loop immediately, and the control of the program moves to the next statement following the loop.
It is almost always used with decision-making statements (Java if…else Statement).
Here is the syntax of the break statement in Java:
break;How break statement works?
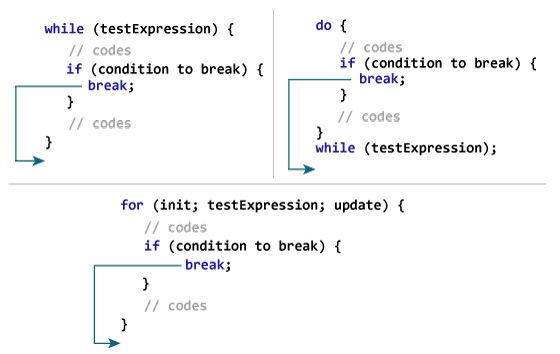
Example 1: Java break statement
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
// for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) {
// if the value of i is 5 the loop terminates
if (i == 5) {
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}Output:
1 2 3 4
In the above program, we are using the for loop to print the value of i in each iteration.
Here, notice the statement,
if (i == 5) {
break;
}This means when the value of i is equal to 5, the loop terminates. Hence we get the output with values less than 5 only.
Example 2: Java break statement
The program below calculates the sum of numbers entered by the user until user enters a negative number.
import java.util.Scanner;
class UserInputSum{
public static void main(String[] args){
Double number, sum = 0.0;
// create an object of Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
// takes double input from user
number = input.nextDouble();
// if number is negative the loop terminates
if (number < 0.0) {
break;
}
sum += number;
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}
Output:
Enter a number: 3.2 Enter a number: 5 Enter a number: 2.3 Enter a number: 0 Enter a number: -4.5 Sum = 10.5
In the above program, the test expression of the while loop is always true. Here, notice the line,
if (number < 0.0) {
break;
}This means when the user input negative numbers, the while loop is terminated.
Java break and Nested Loop
In the case of nested loops, the break statement terminates the innermost loop.

Here, the break statement terminates the innermost while loop, and control jumps to the outer loop.
Labeled break Statement
Till now, we have used the unlabeled break statement. It terminates the innermost loop and switch statement. However, there is another form of break statement in Java known as the labeled break.
We can use the labeled break statement to terminate the outermost loop as well.

As you can see in the above image, we have used the label identifier to specify the outer loop. Now, notice how the break statement is used (break label;).
Here, the break statement is terminating the labeled statement (i.e. outer loop). Then, the control of the program jumps to the statement after the labeled statement.
Here’s another example:
while (testExpression) {
// codes
second:
while (testExpression) {
// codes
while(testExpression) {
// codes
break second;
}
}
// control jumps here
}In the above example, when the statement break second; is executed, the while loop labeled as second is terminated. And, the control of the program moves to the statement after the second while loop.
Example 3: labeled break Statement
class LabeledBreak{
public static void main(String[] args){
// the for loop is labeled as first
first:
for( int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
// the for loop is labeled as second
second:
for(int j = 1; j < 3; j ++ ) {
System.out.println("i = " + i + "; j = " +j);
// the break statement breaks the first for loop
if ( i == 2)
break first;
}
}
}
}Output:
i = 1; j = 1 i = 1; j = 2 i = 2; j = 1
In the above example, the labeled break statement is used to terminate the loop labeled as first. That is,
first:
for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {...}Here, if we change the statement break first; to break second; the program will behave differently. In this case, for loop labeled as second will be terminated. For example,
class LabeledBreak{
public static void main(String[] args){
// the for loop is labeled as first
first:
for( int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
// the for loop is labeled as second
second:
for(int j = 1; j < 3; j ++ ) {
System.out.println("i = " + i + "; j = " +j);
// the break statement terminates the loop labeled as second
if ( i == 2)
break second;
}
}
}
}Output:
i = 1; j = 1 i = 1; j = 2 i = 2; j = 1 i = 3; j = 1 i = 3; j = 2 i = 4; j = 1 i = 4; j = 2
Note: The break statement is also used to terminate cases inside the switch statement.
Java tutorials for Beginners – Java break Statement
Disclaimer: The information and code presented within this recipe/tutorial is only for educational and coaching purposes for beginners and developers. Anyone can practice and apply the recipe/tutorial presented here, but the reader is taking full responsibility for his/her actions. The author (content curator) of this recipe (code / program) has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information was correct at time of publication. The author (content curator) does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss, damage, or disruption caused by errors or omissions, whether such errors or omissions result from accident, negligence, or any other cause. The information presented here could also be found in public knowledge domains.
